Writing a basic Time-of-the-Day (TOD) server is a good experiment for learning basic network programming concepts. A TOD server listens for incoming network connections and responds with the current date and time.
Steps to Implement a TOD Service on a Server
- Create a Socket: Set up a TCP socket to listen for incoming connections.
- Bind the Socket: Bind the socket to a specific IP address and port.
- Listen for Connections: Set the socket to listen for incoming connection requests.
- Accept Connections: Accept incoming client connections and handle them.
- Send the Time: Send the current date and time to the connected client.
- Close the Connection: Close the connection after sending the data.
Code snippet
complete example of a simple ToD service written in C can be found at below
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <time.h>
#define PORT 45000 // The port number on which the ToD service will listen
#define BUFFER_SIZE 128 // variable size buffer
int main() {
int server_fd, client_fd;
struct sockaddr_in server_addr, client_addr;
socklen_t client_addr_len = sizeof(client_addr);
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
time_t current_time;
struct tm *local_time;
int bytes_sent;
// Create a socket
if ((server_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Prepare the sockaddr_in structure
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; // Bind to all available interfaces including lo interface
server_addr.sin_port = htons(PORT); // Port number in network byte order
// Bind the socket to the address and port
if (bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr)) == -1) {
perror("bind");
close(server_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Listen for incoming connections
if (listen(server_fd, 5) == -1) {
perror("listen");
close(server_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Server listening for CLIENT request on port %d...\n", PORT);
while (1) {
// Accept an incoming connection
if ((client_fd = accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &client_addr_len)) == -1) {
perror("accept");
close(server_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Get the current time
current_time = time(NULL);
local_time = localtime(¤t_time);
// copy the formatted time into buffer
snprintf(buffer, BUFFER_SIZE, "Current time: %s", asctime(local_time));
// Send copied buffer to the client
bytes_sent = send(client_fd, buffer, strlen(buffer), 0);
if (bytes_sent == -1) {
perror("send");
}
// current client requested connection closed
close(client_fd);
}
// server socket is closed
close(server_fd);
return 0;
}
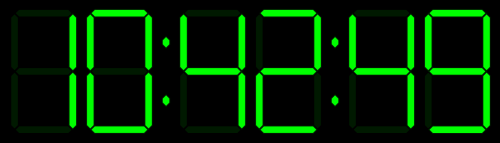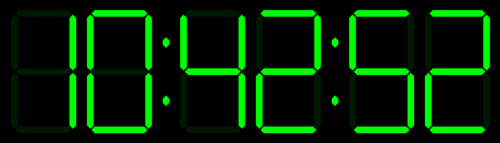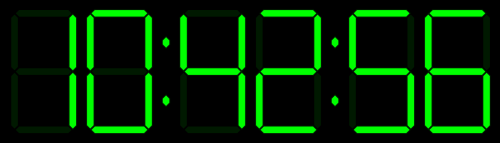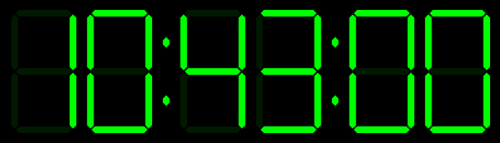
Tick Tick Tick …
simplify above code
- Socket Creation:
server_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);Creates a TCP socket.
Wondering why we didn’t choose UDP sockets ? - Binding:
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(PORT);
bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
Binds the socket to all available interfaces on the specified port. - Listening:
listen(server_fd, 5);Sets the socket to listen for incoming connections, with a backlog queue size of 5
use below command on Linux to know more about listen system call
man listen - Accepting Connections:
client_fd = accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &client_addr_len);
Accepts an incoming connection from a client. - Sending the Time:
current_time = time(NULL);local_time = localtime(¤t_time);snprintf(buffer, BUFFER_SIZE, "Current time: %s", asctime(local_time)); send(client_fd, buffer, strlen(buffer), 0);
Retrieves the current time, formats it, and sends it to the client. - Closing Connections:
close(client_fd); close(server_fd);
Closes the client connection and server socket.
run services on server
- Compile the Code
gcc -o tod_daemon tod_server.c - Run the Server:
./tod_daemon use “netstat -tulpen” command to check/verify whether process is listening on the port or not - Connect to the Server: Send client request to fetch the ToD and You should see the current date and time displayed by the server.
Please write your own TOD client in C language to test the ToD service.
